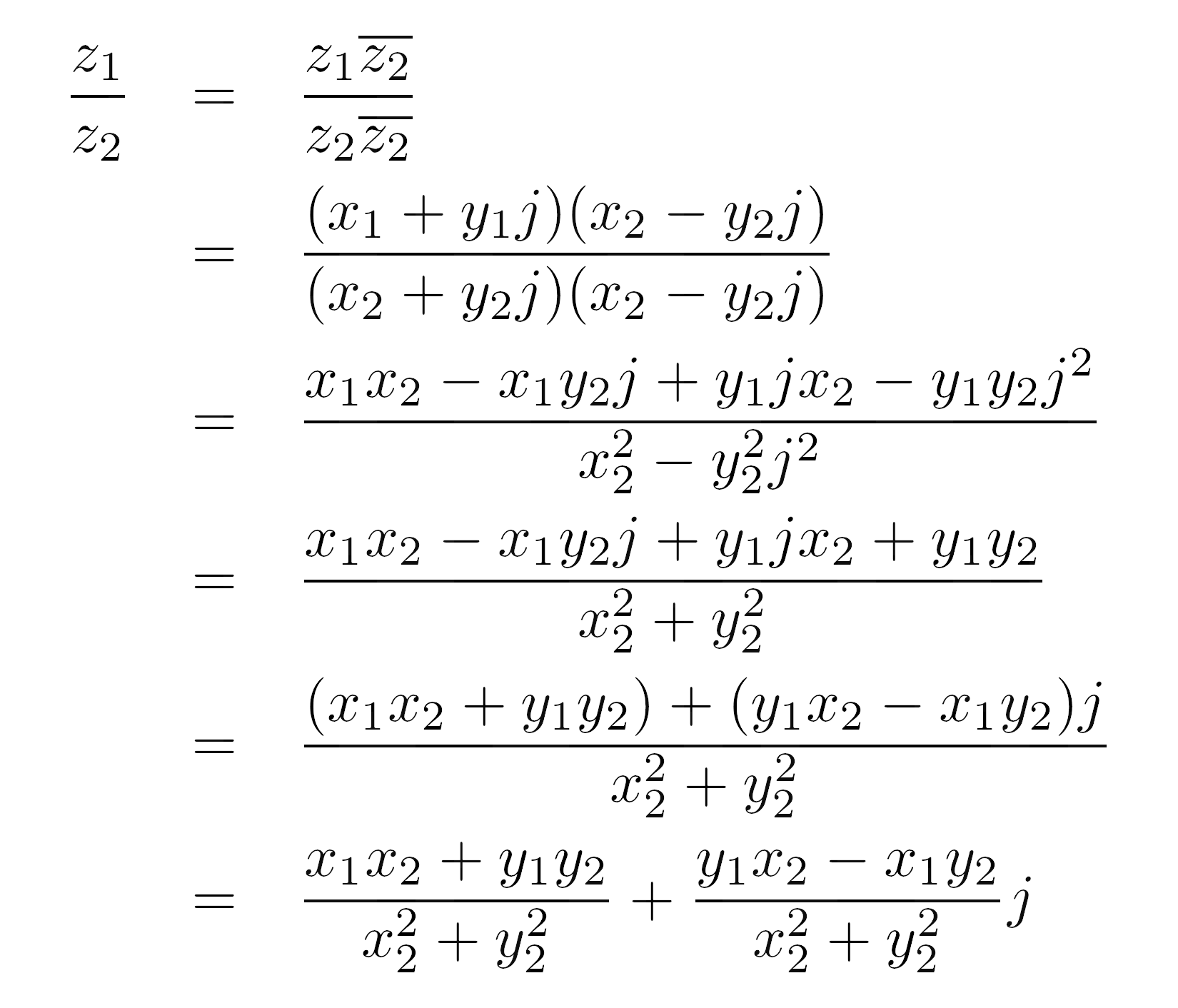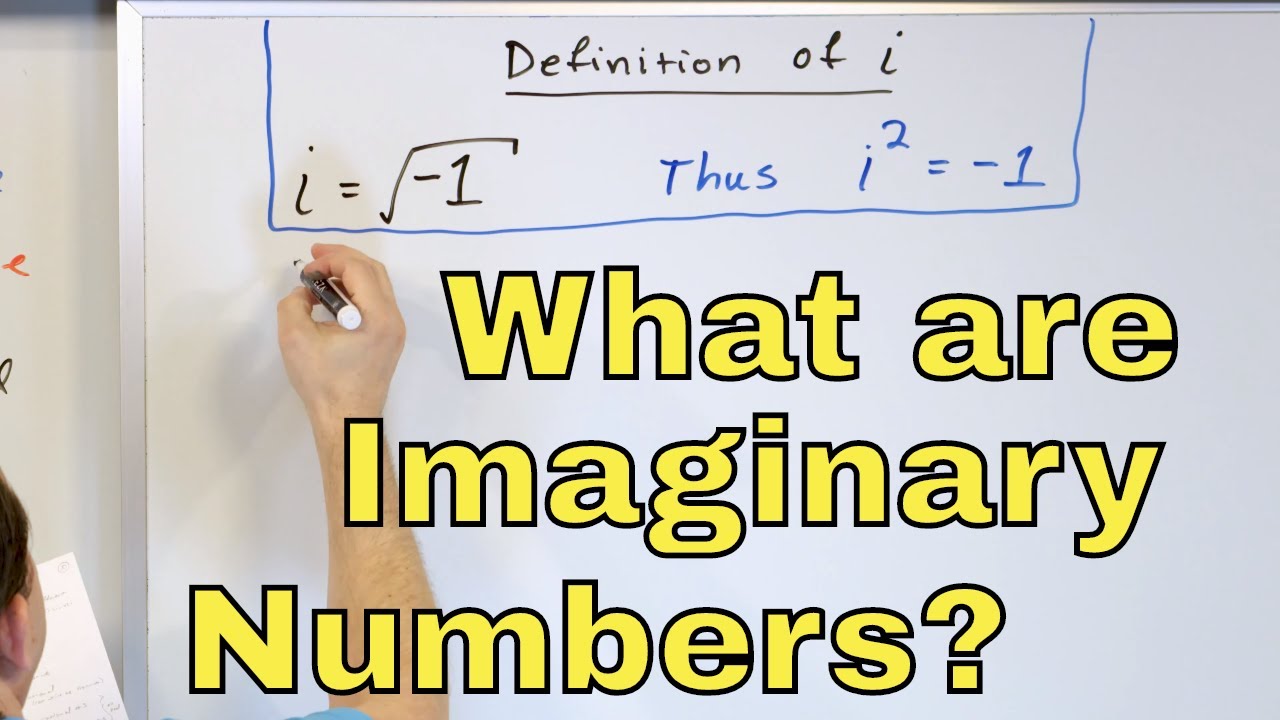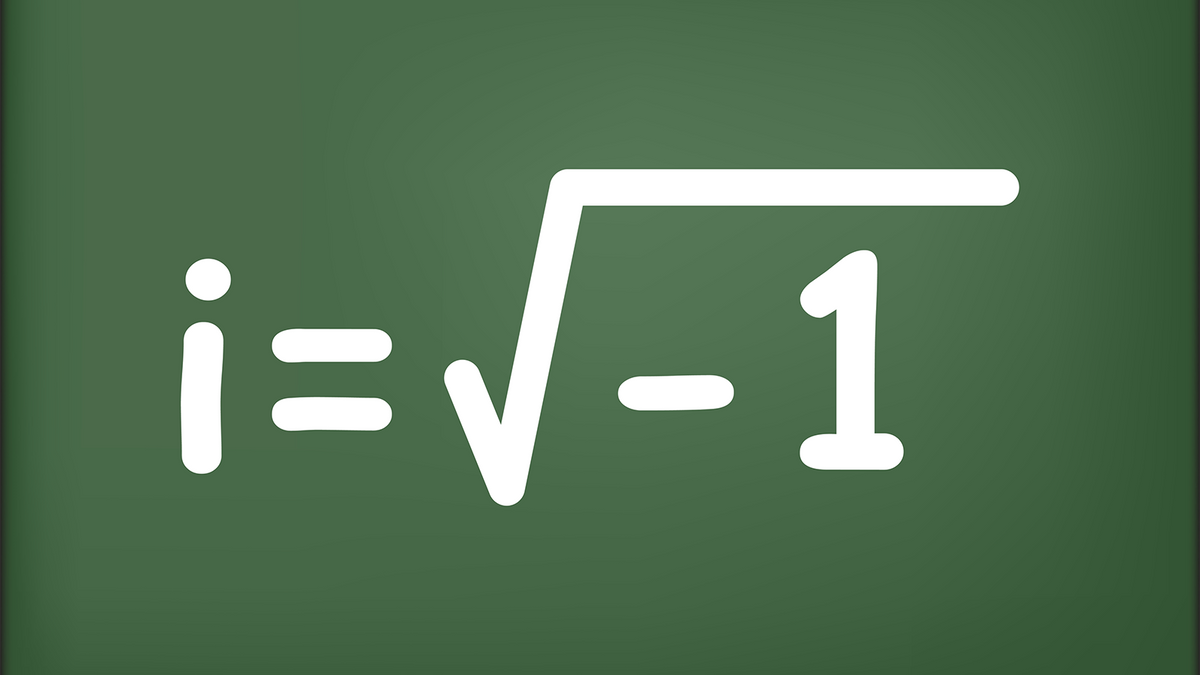Smart Tips About How To Write Imaginary Numbers

Learn how to write and add, subtract, multiply and divide imaginary numbers with examples and rules.
How to write imaginary numbers. To multiply two complex numbers z1 = a + bi and z2 = c + di, use the formula: Explain why we can write z as.
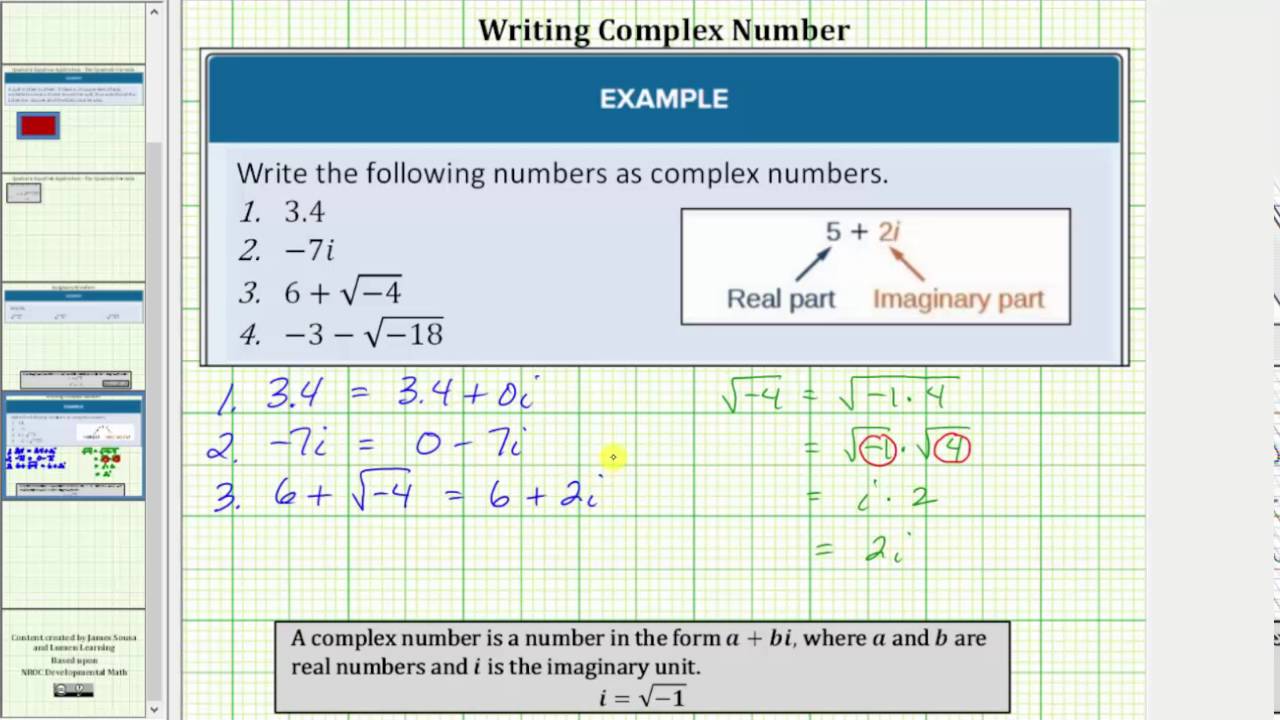
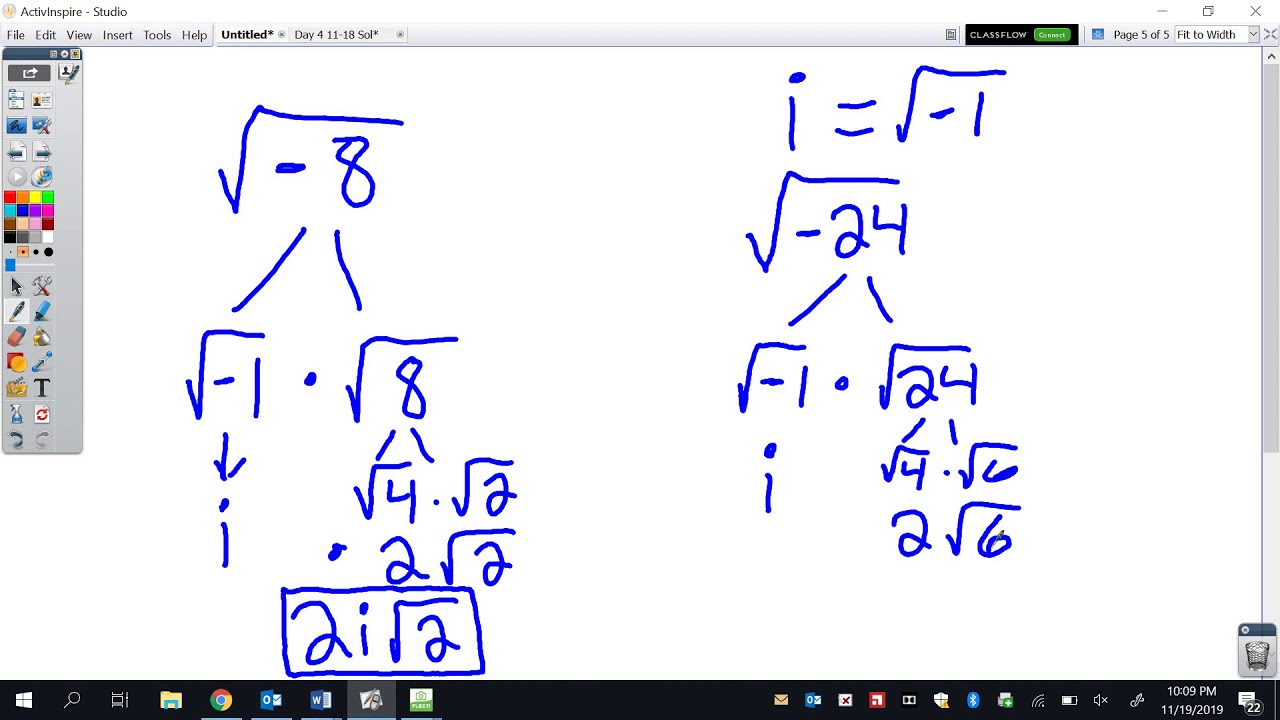
So, using properties of radicals, i2 =(√−1)2 = −1 i 2 = ( − 1) 2 = − 1. In the novel the da. Examples of imaginary numbers:
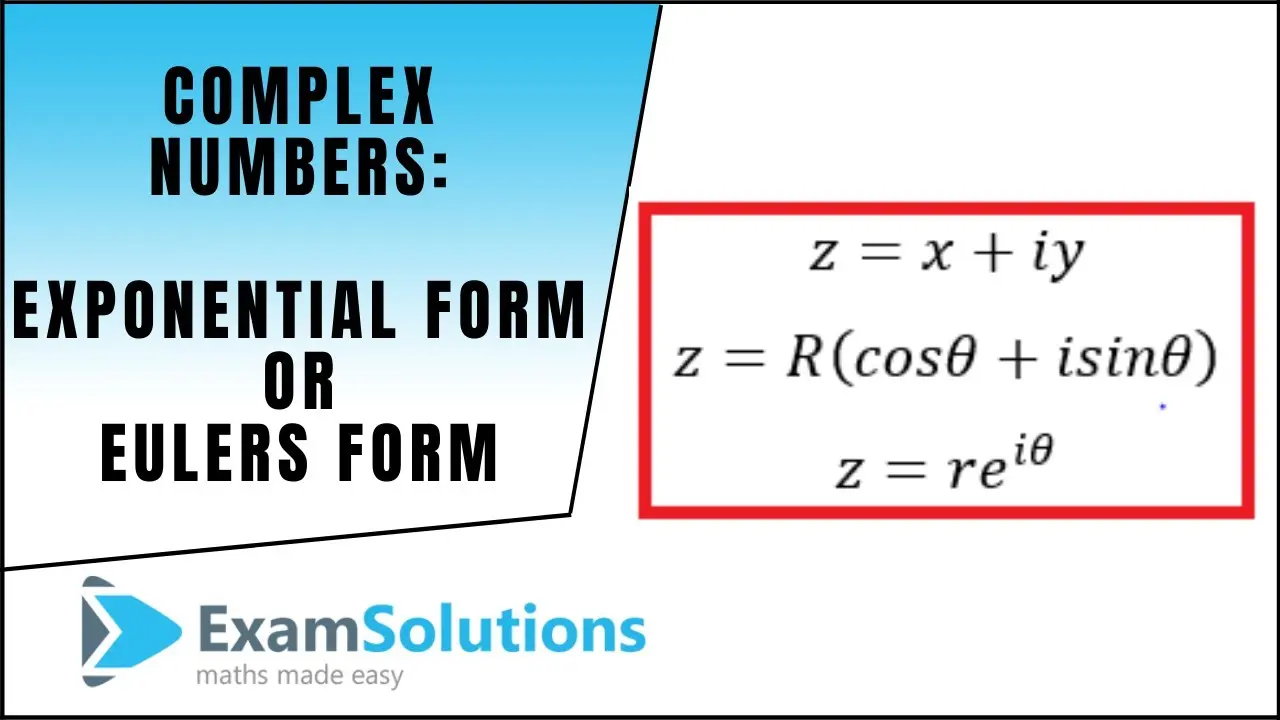
A (purely) imaginary number can be written as a real number multiplied by the imaginary unit i (equal to the square root ), i.e., in the form. (5.2.1) z = r ( cos ( θ) + i sin ( θ)). Square roots of negative numbers can be simplified using.
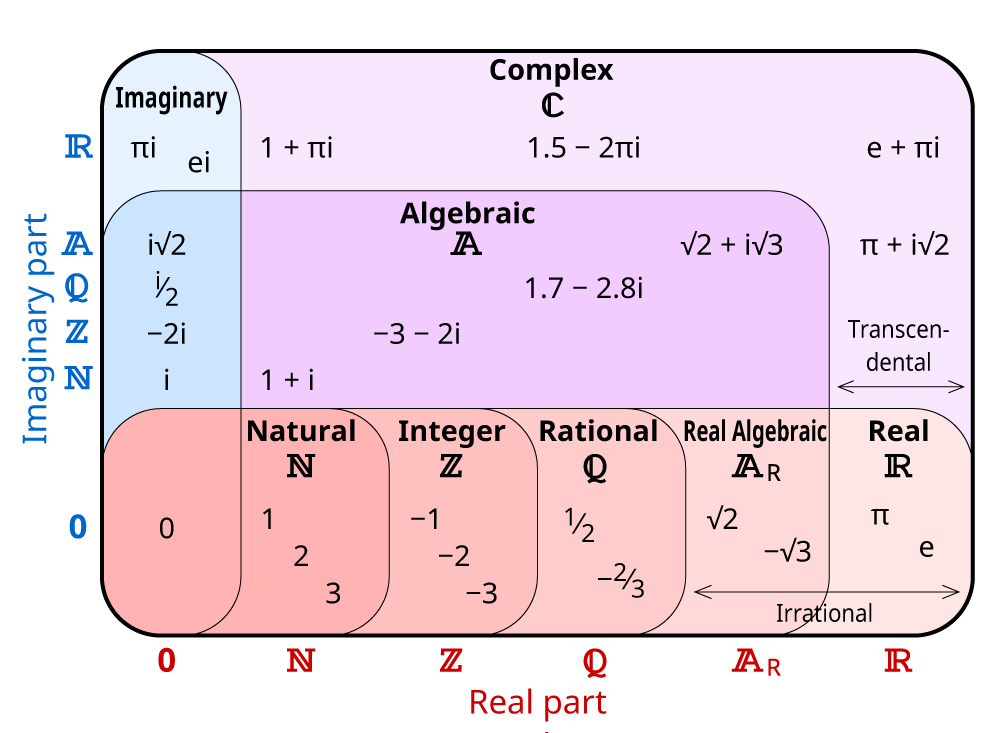
Plotting a complex number \(a+bi\) is similar to plotting a real number, except that the horizontal axis represents the real part of the number, \(a\), and the vertical axis. Radical expressions and quadratic equations. For example, 3 i , i 5 , and − 12 i.
Imaginary numbers explained with formula: Intro to the imaginary numbers. Use right triangle trigonometry to write a and b in terms of r and θ.
Geometrically, imaginary numbers are found on the vertical axis of the complex number plane, which allows them to be presented perpendicular to the real axis. Basic examples (3) i formats as : To define your own complex.
In [1]:= out [1]= the typeset form can be entered as ii (for imaginary i): The number i is by no means alone! We can write the square.
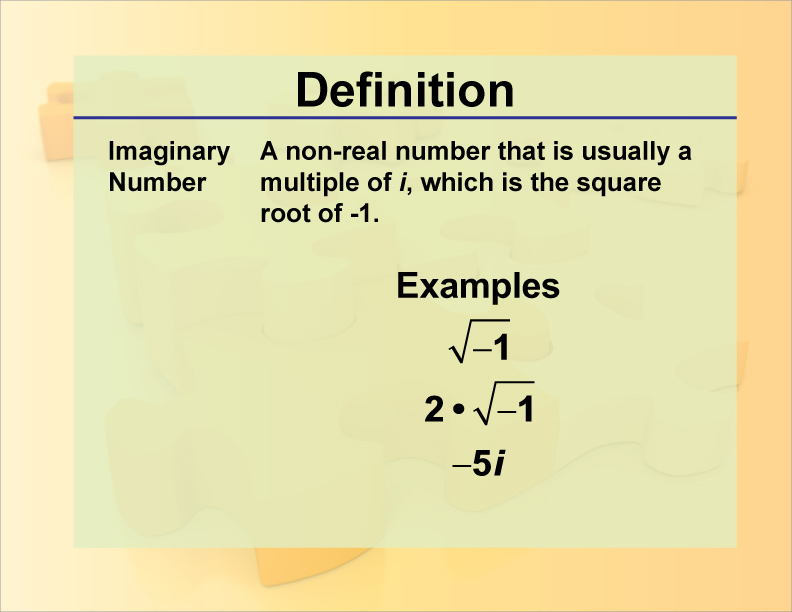
Express imaginary numbers as bi and complex numbers as a+bi a + b i. By taking multiples of this imaginary unit, we can create infinitely many more pure imaginary numbers.
Desmos can add and subtract points just like complex numbers. Imaginary numbers are the numbers that, when squared, yield a result preceded by a negative sign. The imaginary unit i.
And we keep that little i there to remind us we still need to multiply by √−1. Examples include 2 i, −3 i,. I have a method that takes 3 double s and calculates the roots via the quadratic formula: